What Is BLM Land: Understanding The Crucial Role Of Bureau Of Land Management Areas
BLM land refers to vast areas of public land managed by the Bureau of Land Management, a federal agency under the U.S. Department of the Interior. These lands play a critical role in preserving natural resources, supporting recreation, and ensuring sustainable development across the United States. Understanding what BLM land is and how it functions is essential for anyone interested in conservation, outdoor activities, or land management policies.
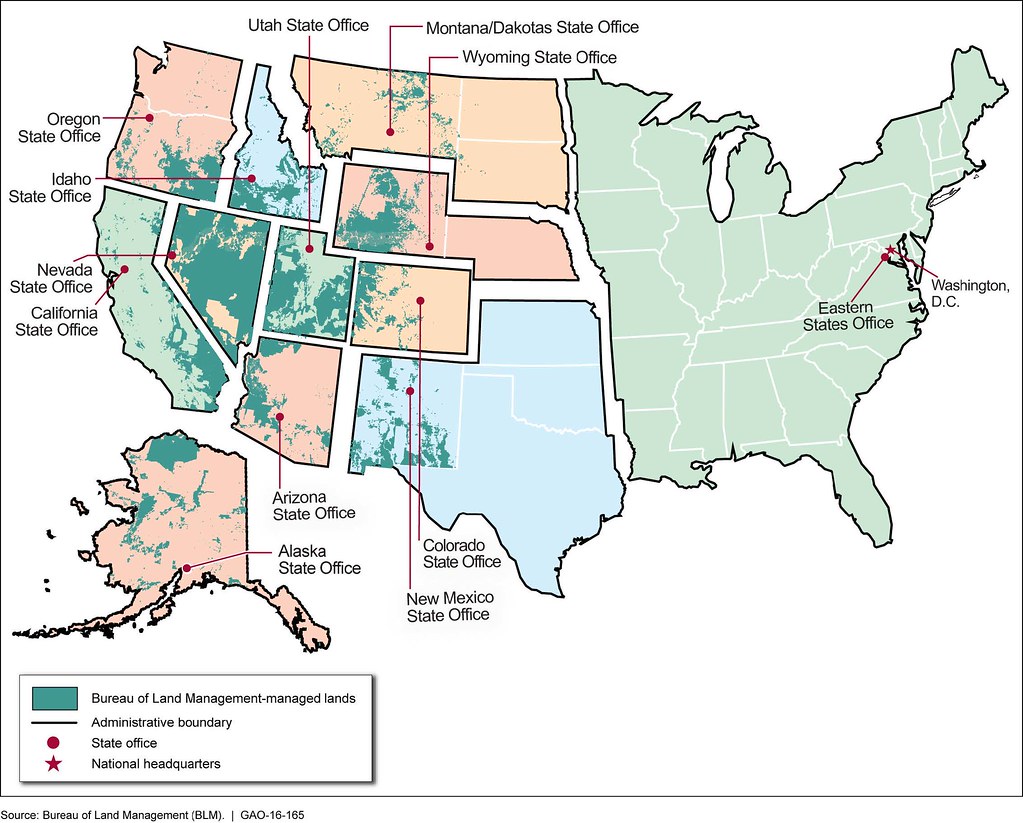
BLM lands cover approximately 245 million acres across the United States, making them one of the largest systems of public lands in the country. These areas are not just open spaces; they serve as vital ecosystems, provide habitats for wildlife, and offer recreational opportunities for millions of Americans. The management of these lands involves balancing conservation efforts with responsible use, ensuring that future generations can enjoy their benefits.
As we delve deeper into this topic, you'll discover the history, purpose, and significance of BLM land, as well as the challenges and opportunities associated with its management. Whether you're an environmentalist, a hiker, or simply someone curious about public land policies, this article will provide you with a comprehensive understanding of what BLM land entails.
Read also:When Is Kat Timpfs Baby Due A Comprehensive Guide
Table of Contents
- Overview of BLM Land
- History of BLM Land
- Purpose of BLM Land
- Management of BLM Land
- Wildlife and Conservation
- Recreational Opportunities on BLM Land
- Challenges in Managing BLM Land
- Sustainability Efforts
- Economic Impact of BLM Land
- Future of BLM Land
Overview of BLM Land
Definition and Extent
BLM land refers to the extensive public land holdings managed by the Bureau of Land Management. These lands span approximately 245 million acres, primarily located in the western United States. The BLM is responsible for overseeing these areas to ensure they are used in a manner that balances conservation, recreation, and economic development.
Types of BLM Land
BLM lands are diverse and include national monuments, wilderness areas, and open rangelands. Each type serves different purposes, from preserving historical sites to providing grazing land for livestock. This diversity highlights the multifaceted role BLM plays in land management.
History of BLM Land
The origins of BLM land date back to the early days of the United States, when the federal government began acquiring large tracts of land through treaties, purchases, and land grants. The General Land Office was initially responsible for managing these lands until it merged with the Grazing Service in 1946 to form the Bureau of Land Management. Over the years, the BLM has evolved to address changing societal needs and environmental concerns.
Purpose of BLM Land
Conservation
One of the primary purposes of BLM land is conservation. These areas serve as critical habitats for numerous plant and animal species, many of which are endangered or threatened. By protecting these ecosystems, the BLM helps maintain biodiversity and ecological balance.
Recreation
BLM lands also offer a wide range of recreational opportunities, including hiking, camping, fishing, and hunting. These activities not only provide enjoyment for individuals but also contribute to local economies through tourism and related businesses.
Management of BLM Land
Strategies and Policies
The BLM employs various strategies and policies to manage its lands effectively. These include resource management plans, environmental assessments, and public involvement processes. By engaging stakeholders and considering scientific data, the BLM aims to make informed decisions that benefit both the environment and the community.
Read also:Erome Home Profile A Comprehensive Guide To The Renowned Luxury Brand
Collaboration with Stakeholders
Effective management of BLM land requires collaboration with a variety of stakeholders, including local governments, indigenous tribes, and conservation organizations. This partnership ensures that diverse perspectives are considered in decision-making processes, leading to more comprehensive and sustainable outcomes.
Wildlife and Conservation
BLM lands are home to a rich variety of wildlife, including species such as the sage grouse, pronghorn antelope, and desert tortoise. The BLM implements conservation programs to protect these species and their habitats, often working with scientists and wildlife experts to develop effective strategies.
Recreational Opportunities on BLM Land
Popular Activities
Recreational activities on BLM land are as diverse as the landscapes themselves. Popular pursuits include off-roading, rock climbing, birdwatching, and photography. Each activity provides unique opportunities for individuals to connect with nature and enjoy the outdoors.
Tips for Visitors
- Check local regulations and guidelines before visiting.
- Practice Leave No Trace principles to minimize environmental impact.
- Be prepared with appropriate gear and supplies for your chosen activity.
Challenges in Managing BLM Land
Managing BLM land comes with several challenges, including balancing competing interests, addressing climate change impacts, and dealing with illegal activities such as vandalism and poaching. The BLM must navigate these issues carefully to ensure the long-term health and viability of its lands.
Sustainability Efforts
Renewable Energy Projects
BLM lands are increasingly being utilized for renewable energy projects, such as wind and solar farms. These initiatives help reduce reliance on fossil fuels and promote a cleaner energy future. The BLM works to ensure that these projects are developed in an environmentally responsible manner.
Water Management
Water is a precious resource in many BLM-managed areas, particularly in arid regions. The BLM implements water management practices to conserve this vital resource and ensure its availability for both wildlife and human use.
Economic Impact of BLM Land
BLM lands contribute significantly to the U.S. economy through activities such as grazing, mining, and recreation. According to the Bureau of Economic Analysis, these lands generate billions of dollars annually and support thousands of jobs across the country. The economic benefits of BLM land extend beyond direct uses, as they also enhance property values and attract businesses to surrounding areas.
Future of BLM Land
As the United States continues to grow and change, the role of BLM land will evolve to meet new challenges and opportunities. Advances in technology, shifts in societal values, and changes in climate will all influence how these lands are managed in the future. The BLM remains committed to adapting its strategies and policies to ensure the continued success and sustainability of its lands.
Conclusion
In summary, BLM land represents a vital component of the United States' public land system. These areas serve multiple purposes, from conservation and recreation to economic development and renewable energy production. By understanding the history, purpose, and management of BLM land, we can appreciate the importance of preserving these valuable resources for future generations.
We invite you to explore BLM lands and experience their beauty and diversity firsthand. Whether you're an outdoor enthusiast, a conservationist, or simply someone interested in learning more about public land management, there is something for everyone to discover. Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below, and don't forget to check out our other articles for more information on related topics.
Data and references for this article were sourced from reputable organizations such as the Bureau of Land Management, the U.S. Department of the Interior, and various scientific studies. For further reading, consider visiting the BLM's official website or consulting peer-reviewed publications on land management and conservation.